Marijuana is an old remedy.
Modern cancer patients aren’t the only people to understand the healing power of marijuana. Marijuana is the name given to the cannabis plant during 20th century prohibition. Cannabis grows wild in warm and tropical climates throughout the world and has been cultivated commercially for eons. Prohibition has given cannabis many other aliases as people developed code. Names like pot, grass, cannabis, weed, hemp, hash, hydro, ganja, and dozens of others all describe the same plant.
Records show marijuana has been used in herbal remedies dating back to the Chin Dynasty in China. Ancient doctors could see the effects of using cannabis as well as today and prescribed it for many maladies. The herb was so powerful that even the Romans put it in their medical texts.
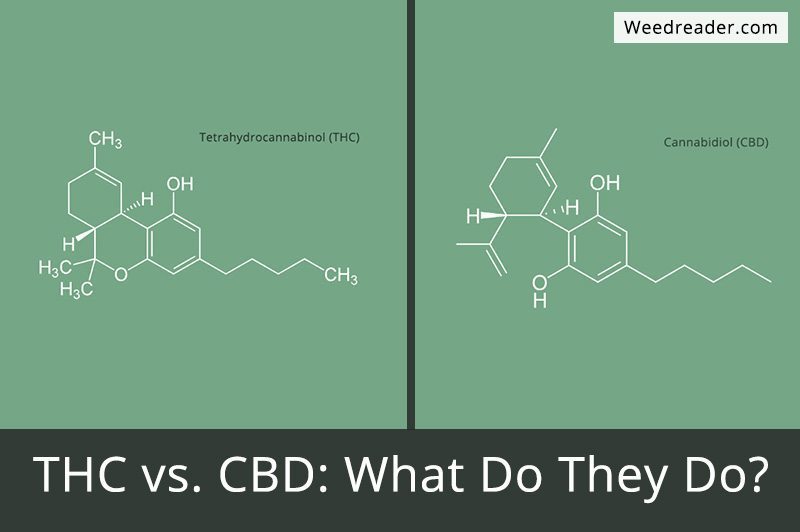
Scientists have identified many biologically active components in marijuana that are the main reason it is so useful medically. These compounds are called cannabinoids. The two most studied of the hundred or so cannabinoids are delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and cannabidiol (CBD). Other cannabinoids are being studied but haven’t had the same amount of press or research put into them.
Is marijuana a legal treatment?
 At this time, the US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) lists marijuana and cannabinoids as Schedule I controlled substances that cannot legally be prescribed, possessed, or sold under federal law. Whole or crude marijuana (including marijuana oil or hemp oil) are also not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical use whatsoever.
At this time, the US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) lists marijuana and cannabinoids as Schedule I controlled substances that cannot legally be prescribed, possessed, or sold under federal law. Whole or crude marijuana (including marijuana oil or hemp oil) are also not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for medical use whatsoever.
State laws have a little bit more play in them and diverge from the federal stance to different degrees. The use of marijuana to treat some medical conditions is legal in many states even though it remains federally banned. Each state has individual rules about how they deal with marijuana so it is important to research the specific rules for your state.
Dronabinol (pharmaceutical THC) and some synthetic cannabinoid drugs like Marinol are approved by the FDA. Marinol is used to relieve nausea and vomiting for chemotherapy patients in addition to being prescribed to AIDS patients for appetite stimulation.
Marijuana is more than THC.
 Different compounds found in marijuana have affect the human body in different ways. For example, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) causes the mental high and can also relieve pain and nausea. At the same time it can reduce inflammation and act as an antioxidant. Cannabidiol (CBD) can help treat seizures, can reduce anxiety and paranoia, and can counteract the “high” caused by THC according to the American Cancer Society.
Different compounds found in marijuana have affect the human body in different ways. For example, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) causes the mental high and can also relieve pain and nausea. At the same time it can reduce inflammation and act as an antioxidant. Cannabidiol (CBD) can help treat seizures, can reduce anxiety and paranoia, and can counteract the “high” caused by THC according to the American Cancer Society.
Different cultivars (strains or types) of marijuana can have varying amounts of the different cannabinoids. The specific ratio of cannabinoids produced by a plant is known as it’s strain profile and can be used to better judge what effects to expect from a specific strain.
The effects of marijuana also change depending on how it enters the body:
- When inactivated or raw cannabis is eaten, the THC is absorbed poorly by the body. Once absorbed, it’s processed by the liver into a second psychoactive compound. The second substance acts on the brain to change mood and/or consciousness differently than THC.
- When marijuana is smoked or vaporized, THC enters the bloodstream quickly, bypassing the liver at first. It is transported to the brain before the liver can convert a large amount of it into the second chemical. Because there is so much less of the second chemical, the high is stronger but fades quicker.
What can marijuana treat?
 A number of studies using small groups of marijuana users found that cannabis can be helpful for treating nausea and vomiting from cancer chemotherapy. A few studies have found that smoked or vaped cannabis can be helpful in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well.
A number of studies using small groups of marijuana users found that cannabis can be helpful for treating nausea and vomiting from cancer chemotherapy. A few studies have found that smoked or vaped cannabis can be helpful in the treatment of neuropathic pain as well.
Smoked marijuana has also helped improve food intake in certain HIV patients during some studies. Clinical trials have also been shown marijuana extract users tended to need less pain medication than others. The pain relieving effects seem to be even better in the non-psychoactive cannabinoid CBD than with THC.
How does marijuana affect cancer?
 According to the American Cancer Society, “…THC and other cannabinoids such as CBD slow growth and/or cause death in certain types of cancer cells growing in lab dishes. Some animal studies also suggest certain cannabinoids may slow growth and reduce spread of some forms of cancer.” While there have been some early clinical trials of cannabinoids in treating cancer, future studies are inevitable.
According to the American Cancer Society, “…THC and other cannabinoids such as CBD slow growth and/or cause death in certain types of cancer cells growing in lab dishes. Some animal studies also suggest certain cannabinoids may slow growth and reduce spread of some forms of cancer.” While there have been some early clinical trials of cannabinoids in treating cancer, future studies are inevitable.
Most studies show cannabinoids can be safe in treating cancer. They do not however seem to help control or cure the disease. Relying on marijuana alone as treatment while avoiding or delaying conventional medical care for any issue (including cancer) may have serious health consequences.
What are the possible harms of marijuana?
 While many insist marijuana can pose no harm to users, it is not true. The most common effect of marijuana is a feeling of euphoria. Yet the complex chemistry of the brain and cannabinoids indicates that there is a lot going on under the hood. Cannabis can lower the user’s control over movement, cause disorientation, and sometimes cause unpleasant thoughts or feelings of anxiety and paranoia. While the majority of users do not experience these negative effects, they are more common in new users who don’t understand their dosing requirements.
While many insist marijuana can pose no harm to users, it is not true. The most common effect of marijuana is a feeling of euphoria. Yet the complex chemistry of the brain and cannabinoids indicates that there is a lot going on under the hood. Cannabis can lower the user’s control over movement, cause disorientation, and sometimes cause unpleasant thoughts or feelings of anxiety and paranoia. While the majority of users do not experience these negative effects, they are more common in new users who don’t understand their dosing requirements.
Smoked marijuana delivers THC and other cannabinoids to the body along with harmful substances. Tar is one of the substances found in both tobacco and cannabis smoke. Heavy users (more than one gram a day) of smoked cannabis also commonly report chronic bronchitis.
Make sure to do research.
Because marijuana plants come in different strains with different levels of active compounds, it can make each experience different. Even with good data from a state certified lab, the effects of a specific strain on a specific user can be very hard to predict. It can take time and experimentation to find the best treatment plan or strain for a specific issue.
Even though cannabis is not chemically addictive (like caffeine or an opioid) people can still become psychologically dependant. Users will not receive the life threatening withdraws like they do from cocaine but they may still feel the conditioned desire to use. Treatments and attitudes toward addiction vary widely across countries and the globe. If you struggle with addiction or are interested in treating any malady, it is best to seek a spectrum of qualified professional help before committing to any treatment plan. Make sure to get more than your own opinion before you make potentially life altering decisions. Thanks for reading.