Trichomes are responsible for producing cannabinoids and terpenes in cannabis.
In fact, almost all of the medical benefit of cannabis comes from trichomes. Compounds like THC and CBD are prescribed by doctors to treat maladies from cancer to headaches.
Trichomes (trichs) are at the heart of the cannabis consumers quest. They are the workhorses that produce the medical miracles that cannabis is known for.
That is because all of the chemicals doctors have discovered in cannabis that treat disease and pain are produced in tiny structures called trichomes. Without trichomes, cannabis wouldn’t be able to help people.
Need to cure some cancer? Cannabis can help because of trichomes. Looking to take the edge off with a quick toke? Better have THC rich trichomes loaded in that bowl or the effort is wasted.
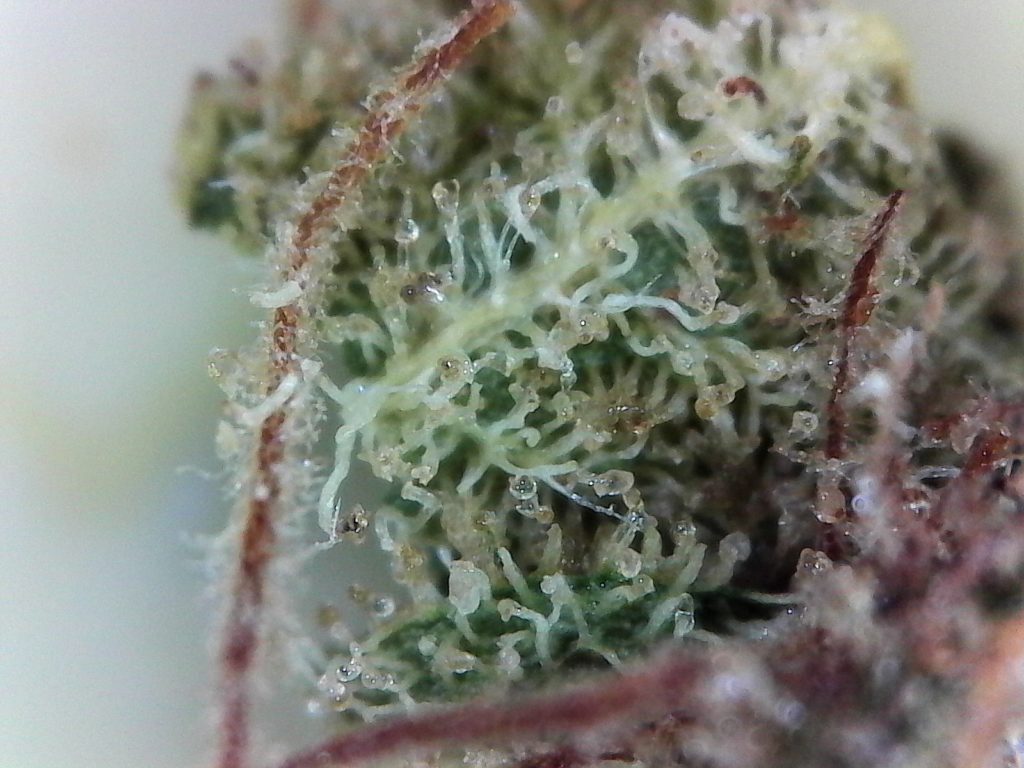

So what are trichomes exactly?
Trichomes are basically tiny chemical factories that cannabis plants create during the flowering process. These factories produce a potent mix of chemicals known as cannabinoids and terpenes.
Most of the 85 cannabinoids found in cannabis are non-psychoactive, meaning they don’t get you high. Yet they do have significant scientific and medical applications that go way beyond getting stoned.
Cannabinoids interact with the endocannabinoid system to produce a variety of positive effects. Research shows that THC and CBD act as neuroprotectants, increase neurogenesis, and can even relieve depression.
Terpenes on the other hand are the chemicals responsible for smells. Limonene is the terpene responsible for the smell of lemons while myrcene is what gives mangos their smell. Yet both terpenes along with a slew of others can be produced by trichomes.
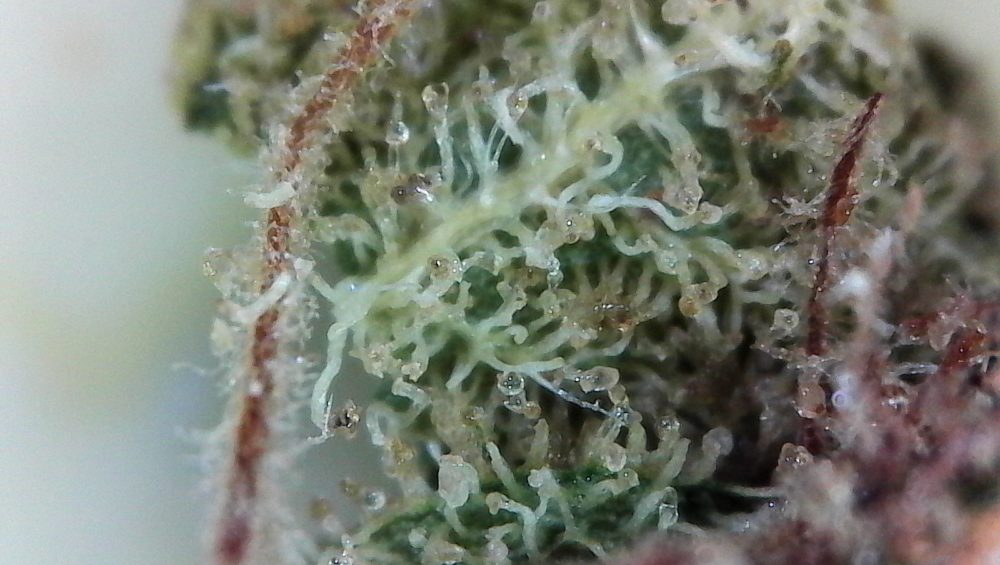
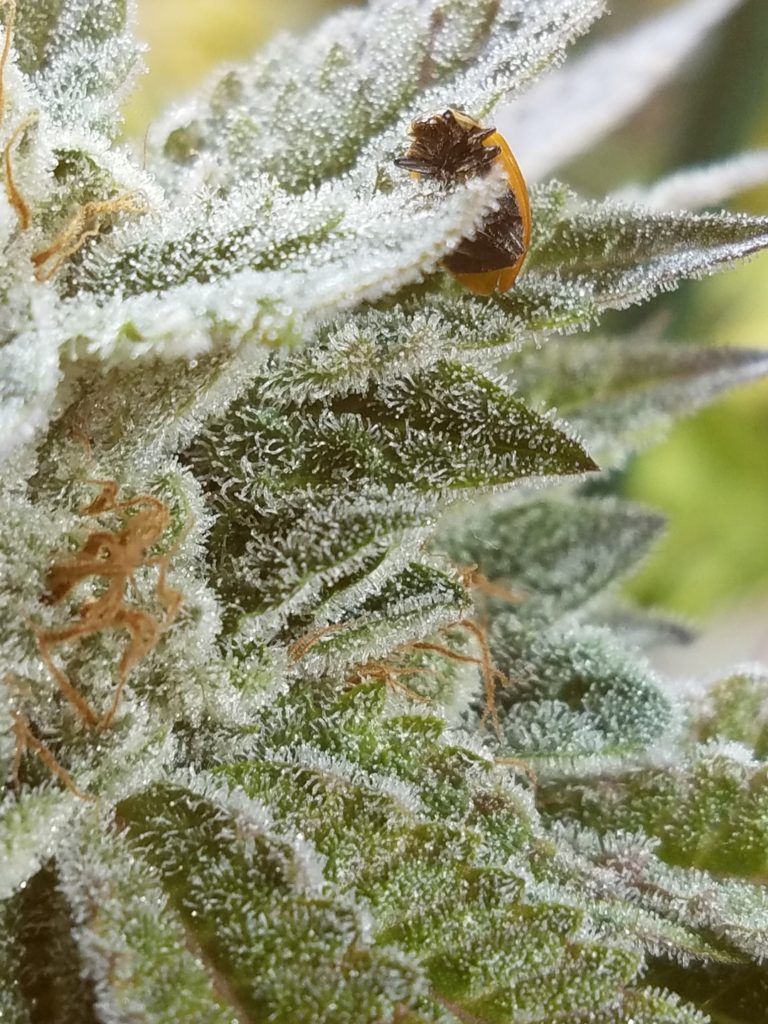
So what does a trichome look like? It is a small hair-like structure produced in the flowers, leaves and stem of cannabis plants. Their main purpose is to protect the plant from dangers like insects or fungus.
Not to be confused with the pistils, trichs are small. Ranging from only 15-500 microns in size, individual trichomes are almost impossible to see with the naked eye. After all, a human hair is only 100 microns across.
Being small doesn’t stop them from creating the potent smell associated with cannabis though. Terpenes produced by trichs can be incredibly powerful, filling the air for miles around with the sweet smell of ganja.

There are many interesting nuances about the science of trichomes.
The chemicals that trichs produce have some amazing properties as well. Cannabinoids like THC and CBD act as neuroprotectants, increase neurogenesis, and relieve depression. Contrary to the fear-mongering of the last few decades, consuming cannabis can protect the body.
And don’t assume that people need to be blazed out of their minds in order to receive a benefit. Most of the 85 cannabinoids found in cannabis are non-psychoactive, meaning they don’t get you high.
In fact, even some forms of THC like THC-A and THC-V don’t get people high. The compounds simply can’t fit into the brains receptors responsible for the feeling of getting high.
Even though a person may not consciously feel the effects, cannabinoids and terpenes produced in trichs have a synergistic quality. The compounds work with each other to magnify the potency of the others.
Take Myrcene as an example. This terpene is found in and responsible for the smell associated with mangos. Myrcene is also one of the most prevalent terpenes in cannabis.
Besides smelling nice, myrcene also helps THC bypass the blood-brain barrier. Basically letting people get high faster and with less cannabis. The effects of cannabis comes down to the ratio of terpenes and cannabinoids that the trichomes have in them at the time.
The specific ratio of cannabinoids and terpenes inside of trichs changes as the terpene develops. This makes timing the harvest a critical step of the process.
Trichome care — what to know about aging and handling of the plant.
So how do people know when a trichome is ready? They look for some of the signs of mature trichomes. These signs include a strong odor and a milky color.
As the cannabis plant enters the flowering process, it starts producing vast quantities of trichs. Strong odors will develop as the initially clear trichomes begin their chemical foundries.
Immature trichomes often have high levels of CBD instead of THC. As a trichome matures, it will begin to cloud up and become milky. Once they have matured, THC becomes the most common cannabinoid.
Life for a trichomes doesn’t stop once it hits maturity though. They continue to develop as long as the plant sticks around. Trichomes that have lived past their prime also continue to change color.
As a trichome moves into old age, the color shifts from milky white to dark amber. The color reflects the chemical decomposition of THC. As the trichomes age, they break down THC into CBN.
How do people get the most value from trichomes?
Trichomes are produced during the flowering process of the cannabis plant. Once produced, trichomes develop over several months before being ready to harvest.
Harvesting before trichomes are fully developed will limit the potency of the final product. That makes the best time to harvest the plant at the final stages of the flowering stage.
Even though all plants are able to produce trichs, they don’t all do it evenly. The female plants produce the significantly more than the males, especially when unpollinated.
Pollinated cannabis plants divert a great deal of energy to producing seeds instead of trichs. This is why many growers remove male plants from their crop before moving into the flowering process.
Things like ensuring adequate nutrients, preventing pollination, high enough levels of light and preventing pests all contribute to heavy trichome yields. Genetics also play a major role in trichome development.
Sometimes strains can produce more trichomes than others. Strains like Durban Poison and Haze take a long time to grow and are known to produce less than strains like Critical Cure and Green Crack.

Other times, a plant needs a little extra push.
Adding extra CO2 to a grow room can also increase the growth rate of cannabis which leads to additional trich production.
Many growers implement a CO2 burner in their rooms to ensure a constant abundance of gas for the plants to use in making more trichomes. This technique can add a significant amount of trichomes compared to other methods.
Growers can also extract the trichs from harvested plants in order to produce a stronger product. The extraction process can be simple or complex but the goal is the same: separate the trichomes from the rest of the plant.
Methods like ice baths, dry sifting and using chemical solvents have all been developed to try and isolate the trichomes. The isolated trichomes are essential for products like BHO, CO2 and PHO.
Truly, the trichome is the key player in the cannabis game. Without trichs and the chemicals they produce, cannabis would not be cultivated around the world.
Hopefully, legalization will continue to progress and more people will get to learn about how important the trichome really is. Thanks for reading.